The Ultimate All-in-One PDF Editor
Edit, OCR, and Work Smarter.
The Ultimate All-in-One PDF Editor
Edit, OCR, and Work Smarter.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology has revolutionized document management, enabling businesses and individuals to convert printed text, handwritten notes, and scanned documents into digital formats that computers can understand and process. With over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created daily, OCR plays a crucial role in making information accessible and actionable.
Whether you're a small business owner drowning in paperwork, a student digitizing research materials, or an enterprise managing massive document archives, understanding OCR technology can dramatically improve your productivity and workflow efficiency. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about OCR, from basic principles to advanced applications.
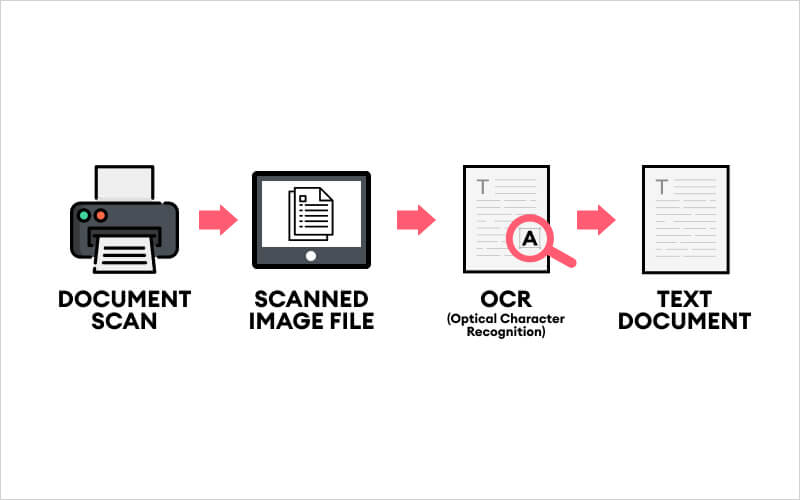
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is the technology that converts images of text – like scanned PDFs, photos, or paper documents – into machine-readable text. In other words, OCR turns the characters in a picture into actual text data. In short, OCR is the bridge between analog documents and digital, searchable text.
As AWS notes, papers like printed contracts or invoices “create challenges” when scanned into images, because the text becomes hidden as an image layer. By applying OCR, that text is extracted and stored as data, enabling search, edit, and analysis. OCR simplifies work: it saves time on data entry and unlocks content hidden in images or scanned files, turning them into editable, searchable text (often called OCR for PDF).

OCR software works through a multi-step pipeline that transforms an image into editable text. The basic stages include image acquisition, preprocessing, character recognition, and post-processing.
There are many OCR tools on the market today, ranging from free mobile apps to enterprise software. The best OCR software depends on your needs, but industry leaders include Adobe Acrobat (Acrobat Pro DC), ABBYY FineReader, and newer AI-based editors like Tenorshare PDNob. These tools vary in price, platforms (Windows/Mac/mobile), and features, but they all aim to accurately convert scanned documents into text.
A well-known PDF editor with built-in OCR. Acrobat can convert scanned PDF pages into searchable, editable PDFs. It supports many languages and integrates with Adobe’s Document Cloud. According to reviews, Adobe’s OCR is highly reliable and works seamlessly on both desktop and mobile (Adobe Scan app). Users can scan documents or images with their phone, and Acrobat will automatically detect and OCR the text.
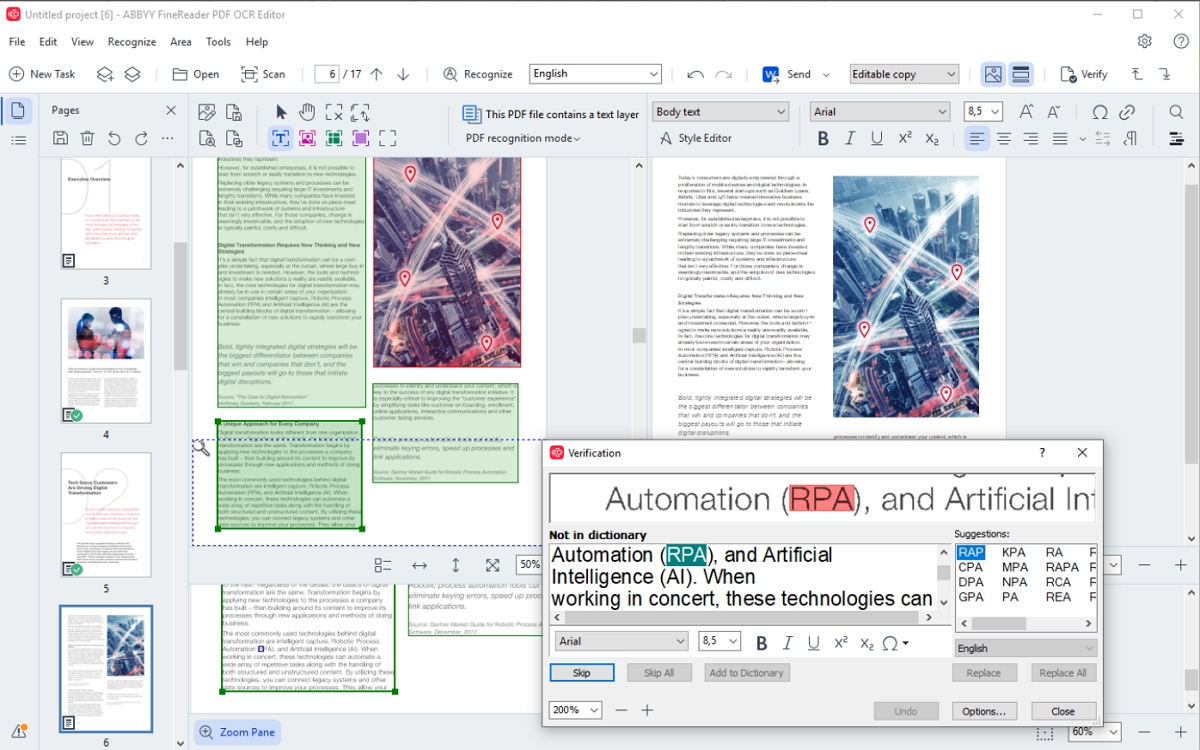
A dedicated OCR application renowned for its accuracy. FineReader uses AI and neural networks to ensure “pinpoint accuracy” in recognizing characters. It supports nearly 200 languages, making it ideal for international or multi-language documents. ABBYY can export to Word, Excel, searchable PDF, and more, preserving layouts. It’s often used in enterprise settings for high-volume scanning and precise text extraction.
A newer OCR-enabled PDF editor that emphasizes AI features. Tenorshare PDNob offers AI-powered OCR claiming over 99% accuracy. It supports 16 languages and can recognize printed, handwritten, and even old book/newspaper fonts. In addition to basic OCR, PDNob includes tools for editing, annotating, and converting PDFs to Word/Excel. Reviews highlight that PDNob is fast, easy to use, and cost-effective as an Adobe alternative. If you want to convert scanned PDFs to text with minimal fuss, tools like PDNob and Acrobat make it straightforward.
There are many others worth noting. Readiris (by IRIS) is known for affordable one-time licensing. Microsoft OneNote and Google Docs also have basic OCR features (you can upload an image to Google Drive and open it as Google Doc to extract text). Open-source Tesseract (backed by Google) powers many free OCR utilities. For cloud/enterprise, AWS Textract, Google Cloud Vision OCR, and Azure Form Recognizer offer OCR as a service via API, useful in automated workflows.
When selecting an OCR solution, it’s important to match features with your needs. Key criteria include:
For many users, accuracy and language support are top priorities. Leading tools like Tenorshare PDNob offer over 99% accuracy and multi-language recognition, ensuring nearly perfect text capture. Simplicity is also important—OCR should be easy to use without special training.
Enterprise users often choose Adobe Acrobat or ABBYY FineReader for advanced features, while small teams or individuals may prefer PDNob or free tools for ease and value. Always test OCR with sample documents before buying. The best OCR software fits your workflow, integrates with your systems, and balances accuracy, usability, and needed features.
The future of OCR is driven by AI and machine learning, improving accuracy and enabling smart data extraction beyond text recognition. Real-time OCR, mobile on-device processing, and cloud services make text capture faster, more private, and scalable. Integration with AI, automation, and blockchain is turning OCR into an intelligent tool for document analysis and secure verification.
Specialized OCR solutions for industries like healthcare and finance will grow, with accuracy nearing perfection. Faster processing, privacy-focused methods, and IoT-enabled automation will streamline workflows. These advances will transform how physical documents become digital, boosting efficiency and enabling new applications.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) transforms images of text into editable, searchable data, saving time and enabling efficient workflows. It’s key for digitizing archives, automating invoices, and making documents easy to search.
Modern OCR uses AI for high accuracy. Leading tools like Adobe Acrobat and ABBYY FineReader set the bar, while Tenorshare PDNob offers powerful AI features and supports many languages with 99% accuracy. Discover the value of OCR today and take a step towards a smarter, paperless workflow.


PDNob PDF Editor Software- Smarter, Faster, Easier
 The END
The END
I am PDNob.
Swift editing, efficiency first.
Make every second yours: Tackle any PDF task with ease.
As Leonardo da Vinci said, "Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication." That's why we built PDNob.
then write your review
Leave a Comment
Create your review for Tenorshare articles
By Jenefey Aaron
2026-02-28 / Knowledge